tags: snort_Windows IDS_Windows IDS
Snort è un software open source che permette di rilevare intrusioni e azioni sospette tramite regole che si possono modificare a piacere, per scaricarlo ci servirà il file .exe che è presente nella cartella CEH o su internet e il driver WinPcap presente sulla macchina, una volta installato andrà a salvare il file di installazione in C:\Snort.
Ora se stai usando la cartella CEH vai in questa cartella E:\CEH-Tools\CEHv13 Module 12 Evading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypots\Intrusion Detection Tools\Snort\snortrules-snapshot-29150\etc copia il file snort.conf e copialo nella cartella C:\Snort\etc sostituendo quello esistente, fai lo stesso con i file so_rules, prepoc_rules e rules presenti nella cartella E:\CEH-Tools\CEHv13 Module 12 Evading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypots\Intrusion Detection Tools\Snort\snortrules-snapshot-29150 e copiali nella cartella C:\Snort.
-
Now, right-click on the Windows Start icon and click Run from the menu.
-
The Run window appears; type cmd in the Open field and click OK to launch command prompt window.
-
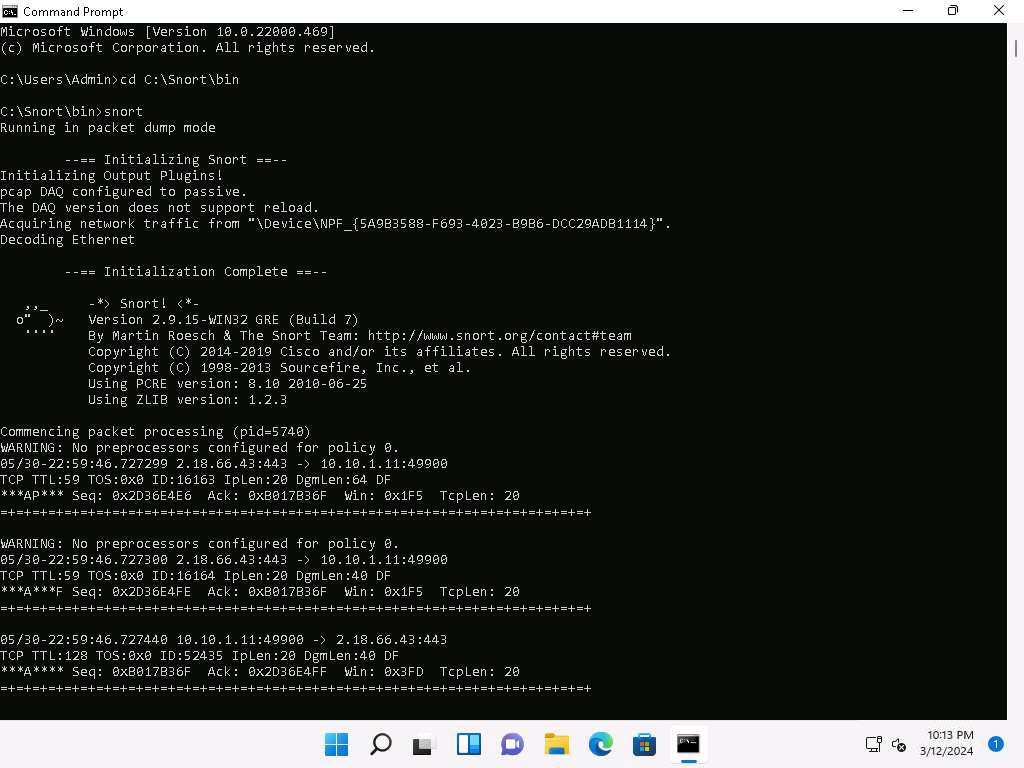
The Command Prompt window appears; type cd C:\Snort\bin and press Enter to access the bin folder in the command prompt. Run snort command to initiate snort.
-
Snort initializes; wait for it to complete. Press Ctrl+C after some time, Snort exits and comes back to C:\Snort\bin.
-
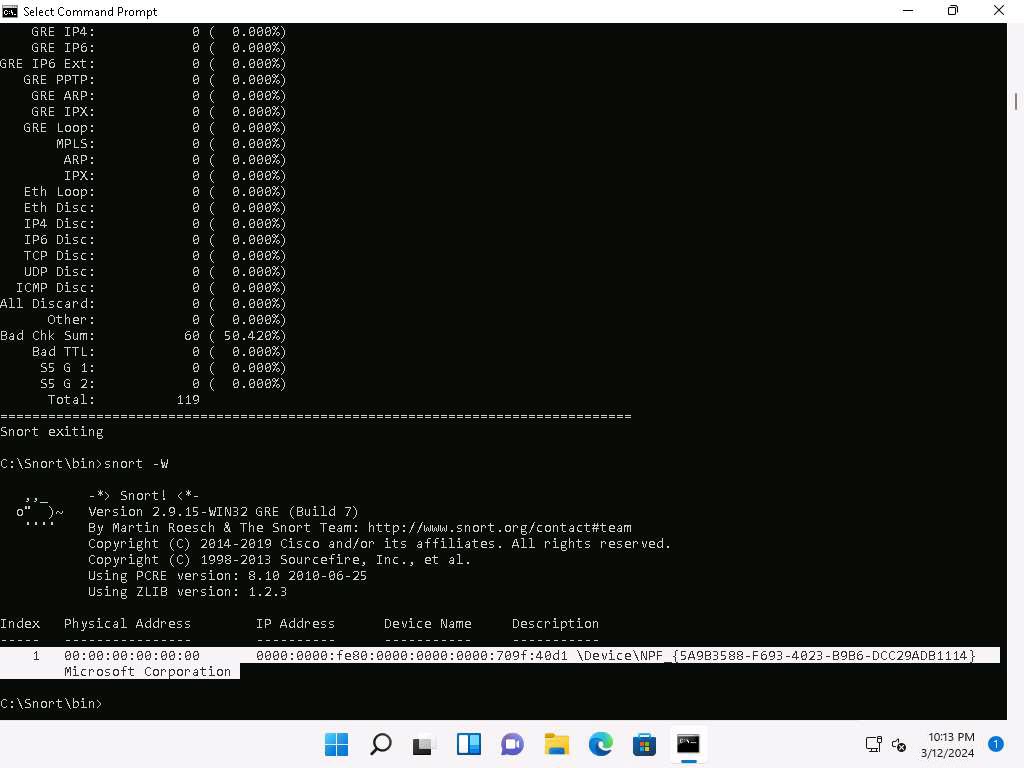
Now type snort -W. This command lists your machine’s physical address, IP address, and Ethernet Drivers, but all are disabled by default.
-
Observe your Ethernet Driver index number and write it down (in this task, it is 1).
-
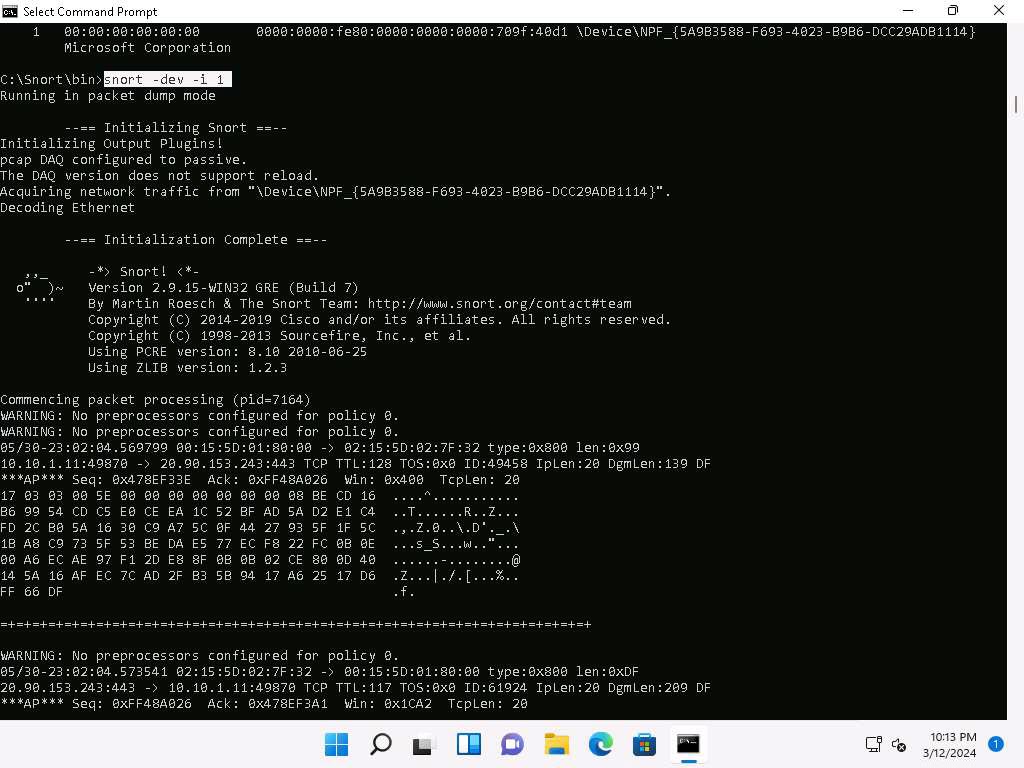
To enable the Ethernet Driver, in the command prompt, run command snort -dev -i 1.
-
You see a rapid scroll text in the command prompt, which means that the Ethernet Driver is enabled and working properly.
-
Leave the Snort command prompt window open, and launch another command prompt window.
-
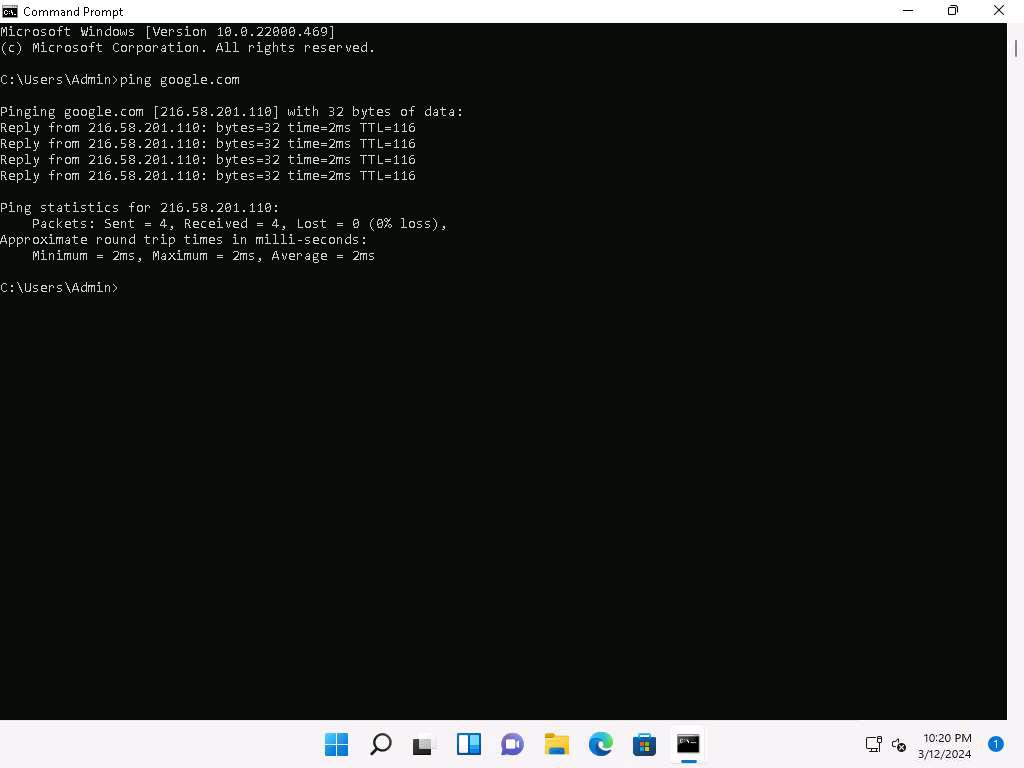
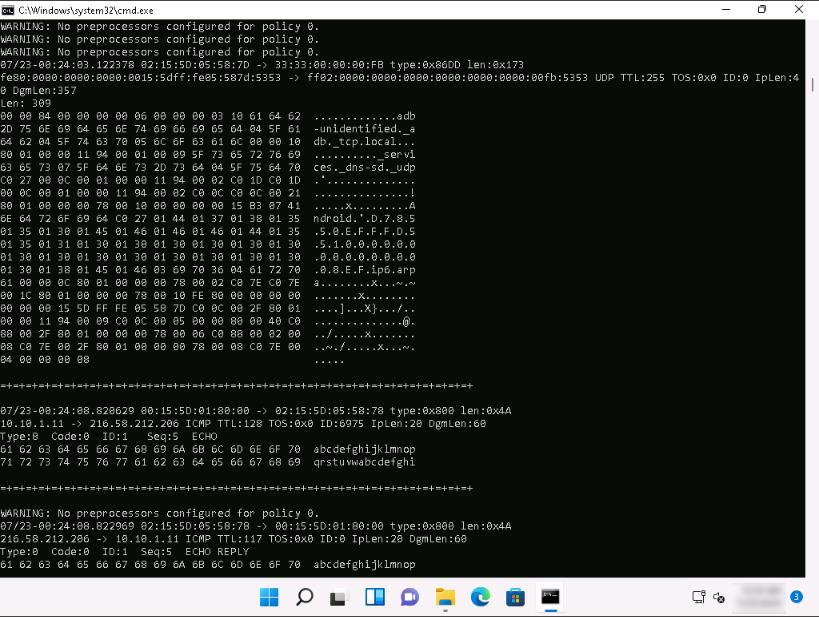
In a new command prompt, run ping google.com command.
-
This ping command triggers a Snort alert in the Snort command prompt with rapid scrolling text.
The Google IP address will differ when you perform this task.
-
Close both command prompt windows. The verification of Snort installation and the triggering alert is complete, and Snort is working correctly in verbose mode.
-
Configure the snort.conf file, located at C:\Snort\etc.
-
Open the snort.conf file with Notepad++.
-
Scroll down to the Step #1: Set the network variables section (Line 41) of the snort.conf file. In the HOME_NET line (Line 45), replace any with the IP addresses of the machine (target machine) on which Snort is running. Here, the target machine is Windows 11 and the IP address is 10.10.1.11.
-
Leave the EXTERNAL_NET any line as it is.
-
If you have a DNS Server, then make changes in the DNS_SERVERS line by replacing $HOME_NET with your DNS Server IP address; otherwise, leave this line as it is.
Here, the DNS server is 8.8.8.8.

-
The same applies to SMTP_SERVERS, HTTP_SERVERS, SQL_SERVERS, TELNET_SERVERS, and SSH_SERVERS.
-
Remember that if you do not have any servers running on your machine, leave the line as it is. DO NOT make any changes in that line.
-
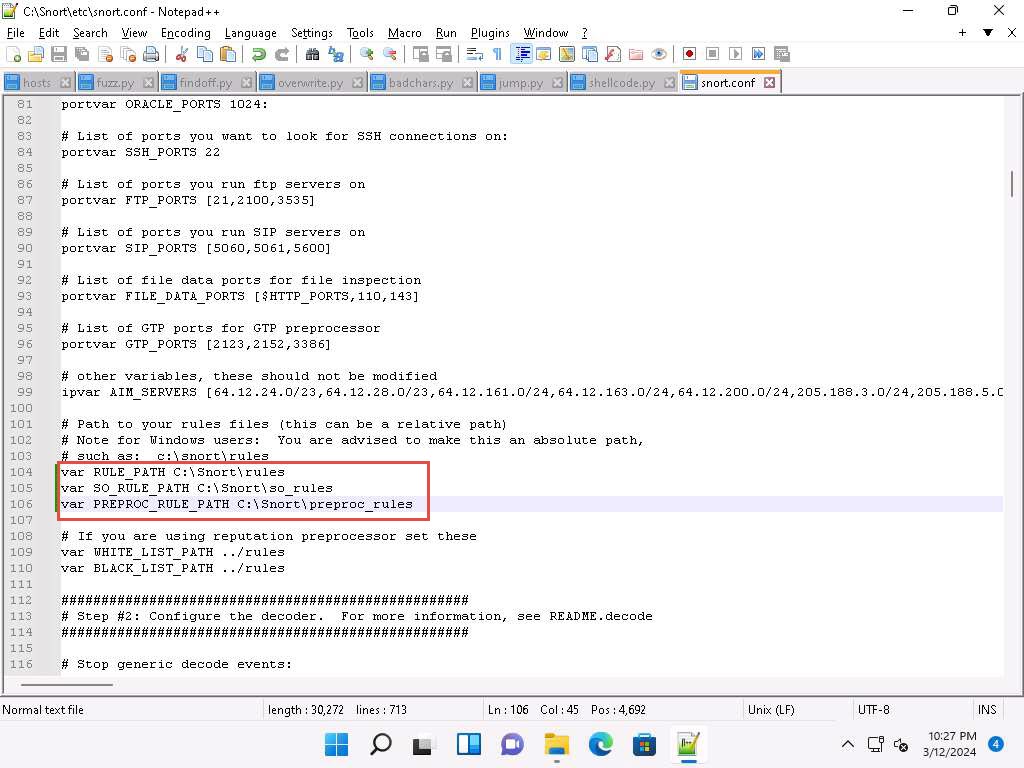
Scroll down to RULE_PATH (Line 104). In Line 104, replace ../rules with C:\Snort\rules in Line 105, replace ../so_rules with C:\Snort\so_rules and in Line 106, replace ../preproc_rules with C:\Snort\preproc_rules.
-
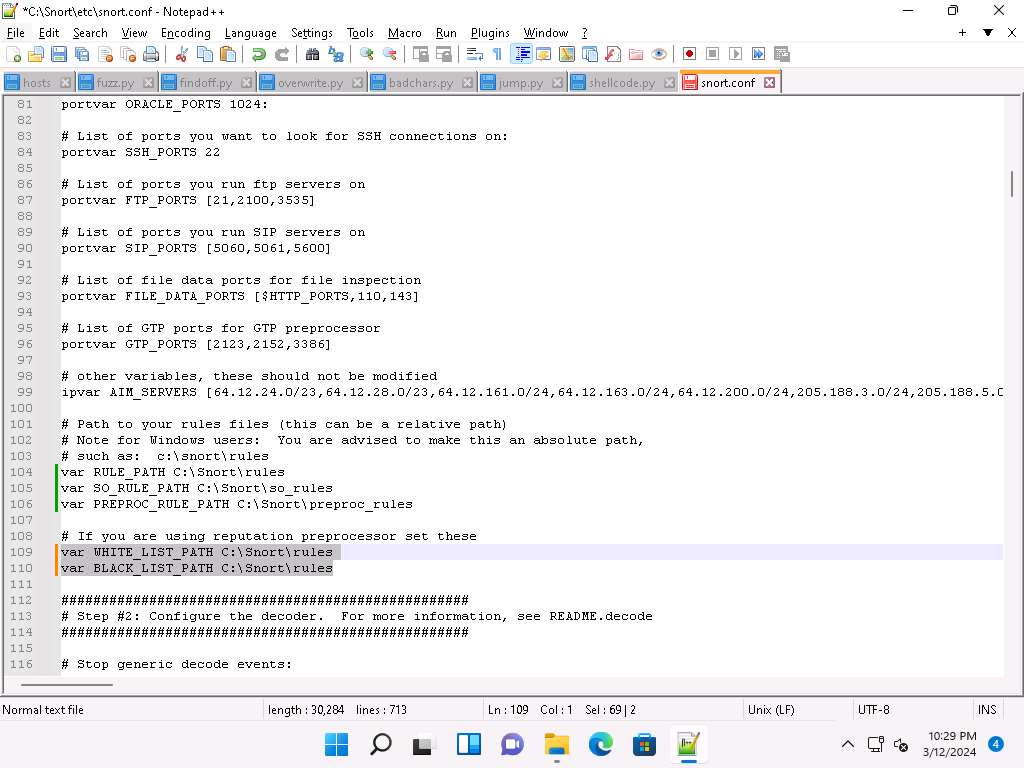
In Lines 109 and 110, replace ../rules with C:\Snort\rules. Minimize the Notepad++ window.
-
Navigate to C:\Snort\rules, and create two text files; name them white_list and black_list and change their file extensions from .txt to .rules.
To create a text file, right-click anywhere inside the rules window and navigate to New ⇒ Text Document.
-
While changing the extension, if any pop-up appears, click Yes.
-
Switch back to Notepad++, scroll down to the Step #4: Configure dynamic loaded libraries section (Line 238). Configure dynamic loaded libraries in this section.
-
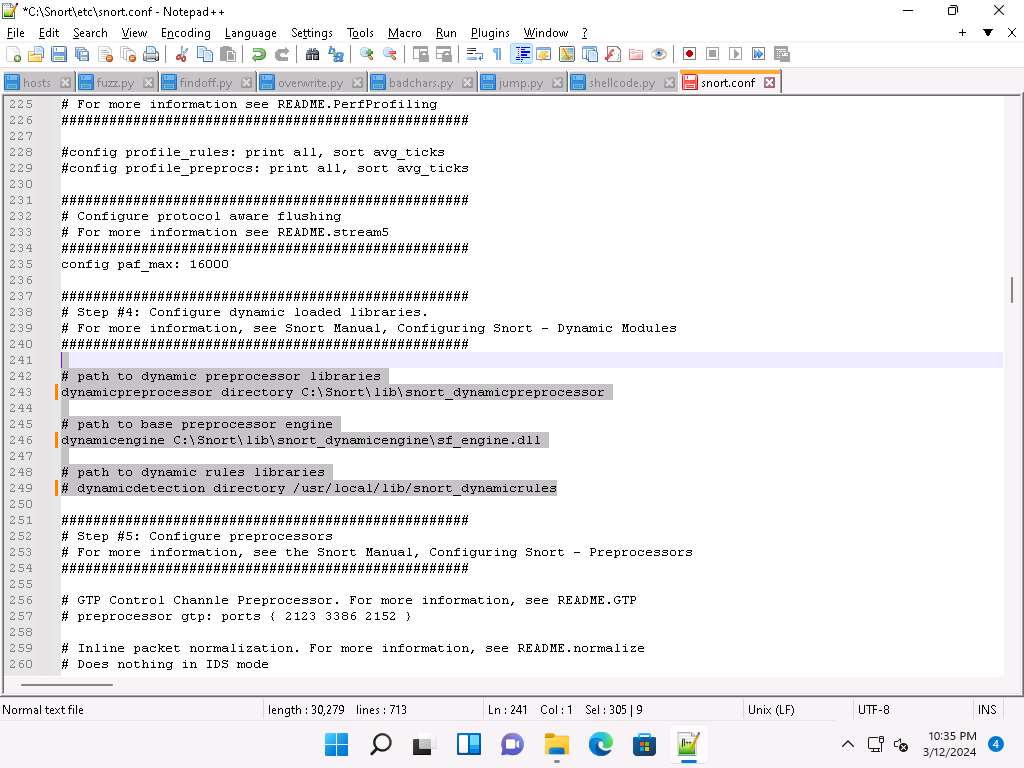
Add the path to dynamic preprocessor libraries (Line 243); replace /usr/local/lib/snort_dynamicpreprocessor/ with your dynamic preprocessor libraries folder location.
-
In this task, the dynamic preprocessor libraries are located at C:\Snort\lib\snort_dynamicpreprocessor.
-
At the path to base preprocessor (or dynamic) engine (Line 246), replace /usr/local/lib/snort_dynamicengine/libsf_engine.so with your base preprocessor engine C:\Snort\lib\snort_dynamicengine\sf_engine.dll.
-
Ensure that the dynamic rules libraries (Line 249) is commented out, as you have already configured the libraries in dynamic preprocessor libraries.
Add (space) in between # and dynamicdetection (Line 249).
-
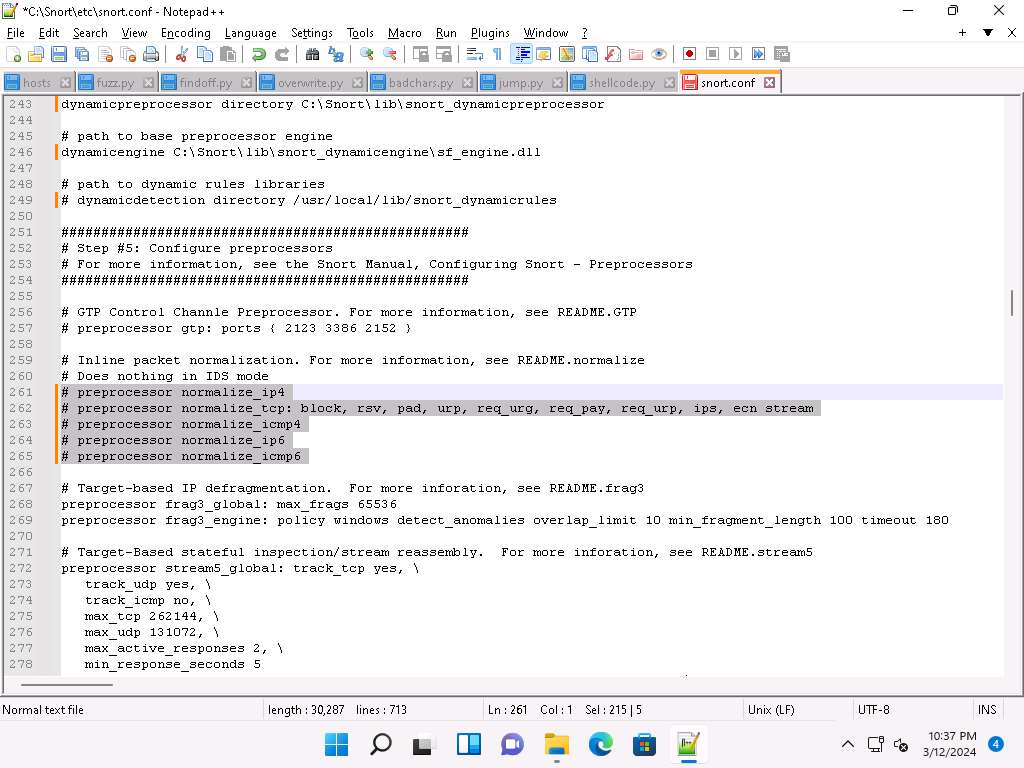
Scroll down to the Step #5: Configure preprocessors section (Line 253), the listed preprocessor. This does nothing in IDS mode, however, it generates errors at runtime.
-
Comment out all the preprocessors listed in this section by adding ‘#’ and (space) before each preprocessor rule (261-265).
To ‘comment out’ is to render a block of code inert by turning it into a comment.
-
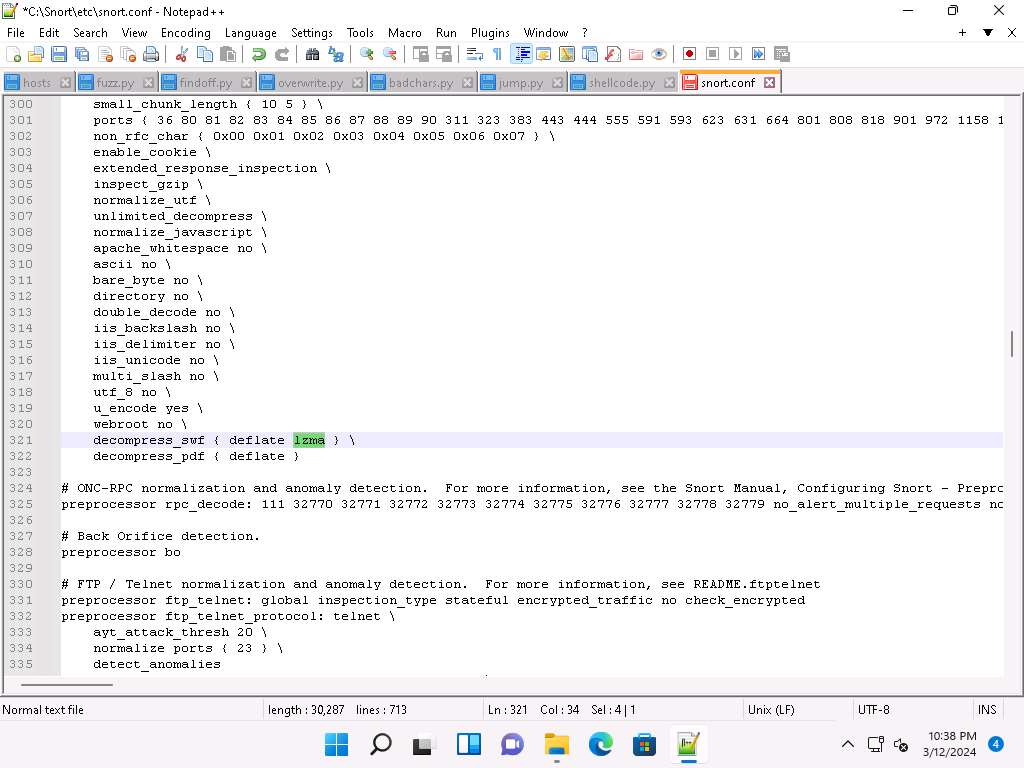
Scroll down to line 321 and delete lzma keyword and a (space).
Make sure you only delete “lzma” keyword.
-
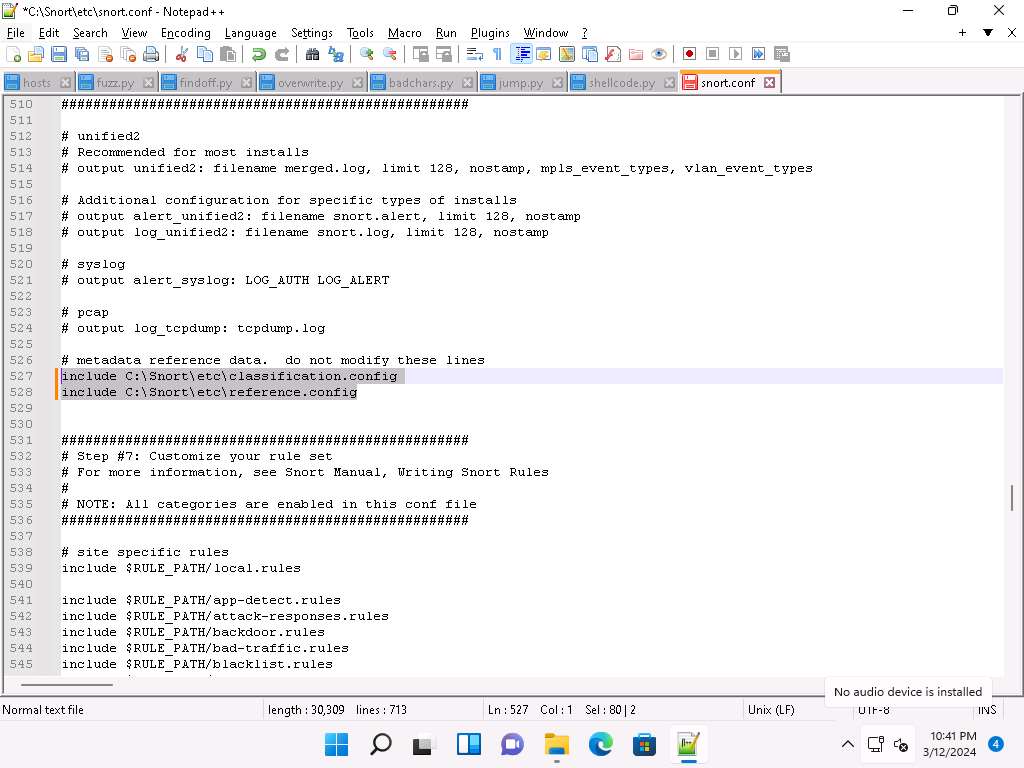
Scroll down to Step #6: Configure output plugins (Line 513). In this step, provide the location of the classification.config and reference.config files.
-
These two files are in C:\Snort\etc. Provide this location of files in the configure output plugins (in Lines 527 and 528) (i.e., C:\Snort\etc\classification.config and C:\Snort\etc\reference.config).
-
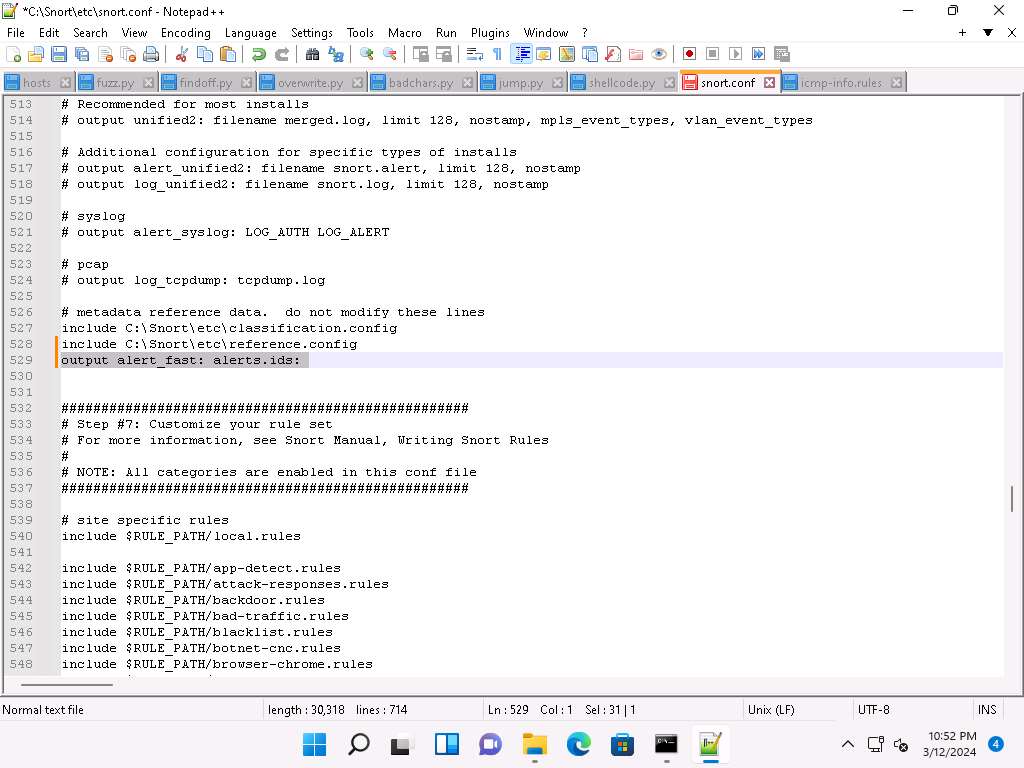
In Step #6, add to line (529) output alert_fast: alerts.ids: this command orders Snort to dump all logs into the alerts.ids file.
-
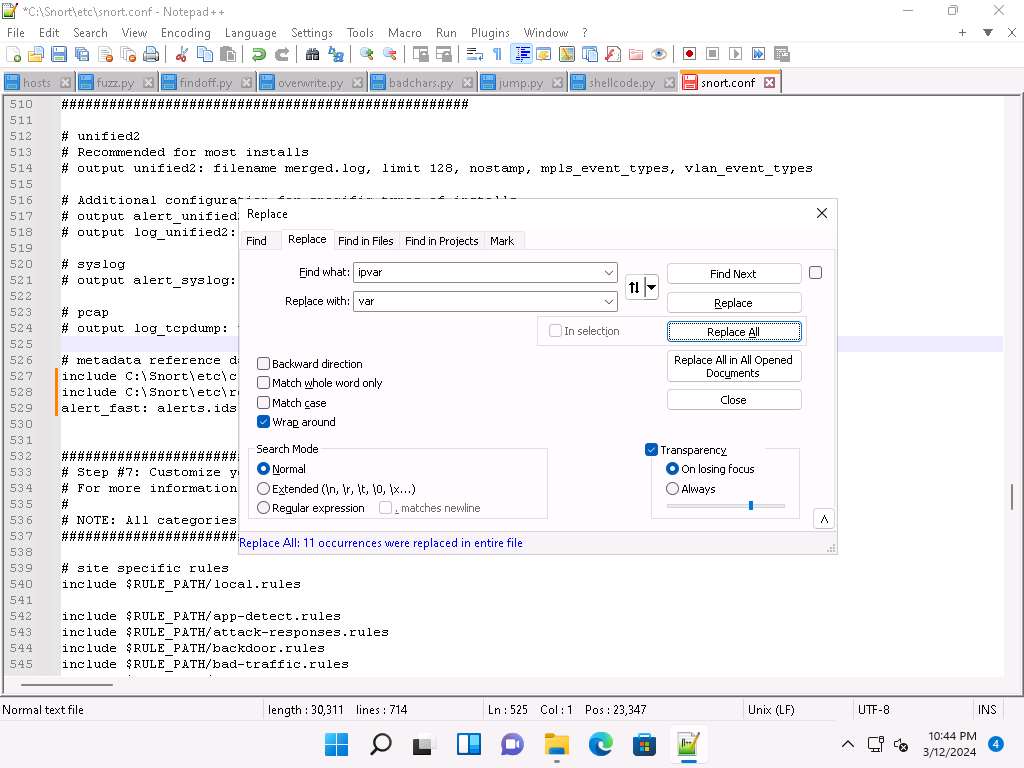
In the snort.conf file, find and replace the ipvar string with var. To do this, press Ctrl+H on the keyboard. The Replace window appears; enter ipvar in the Find what : text field, enter var in the Replace with : text field, and click Replace All.
You will get a notification saying 11 occurrences were replaced.
-
By default, the string is ipvar, which is not recognized by Snort: replace with the var string, and then close the window.
Snort now supports multiple configurations based on VLAN Id or IP subnet within a single instance of Snort. This allows administrators to specify multiple snort configuration files and bind each configuration to one or more VLANs or subnets rather than running one Snort for each configuration required.
-
Click Close to close the Replace window.
-
Save the snort.conf file by pressing Ctrl+S and close Notepad++ window.
-
Before running Snort, you need to enable detection rules in the Snort rules file. For this task, we have enabled the ICMP rule so that Snort can detect any host discovery ping probes directed at the system running Snort.
-
Navigate to C:\Snort\rules and open the icmp-info.rules file with Notepad++.
-
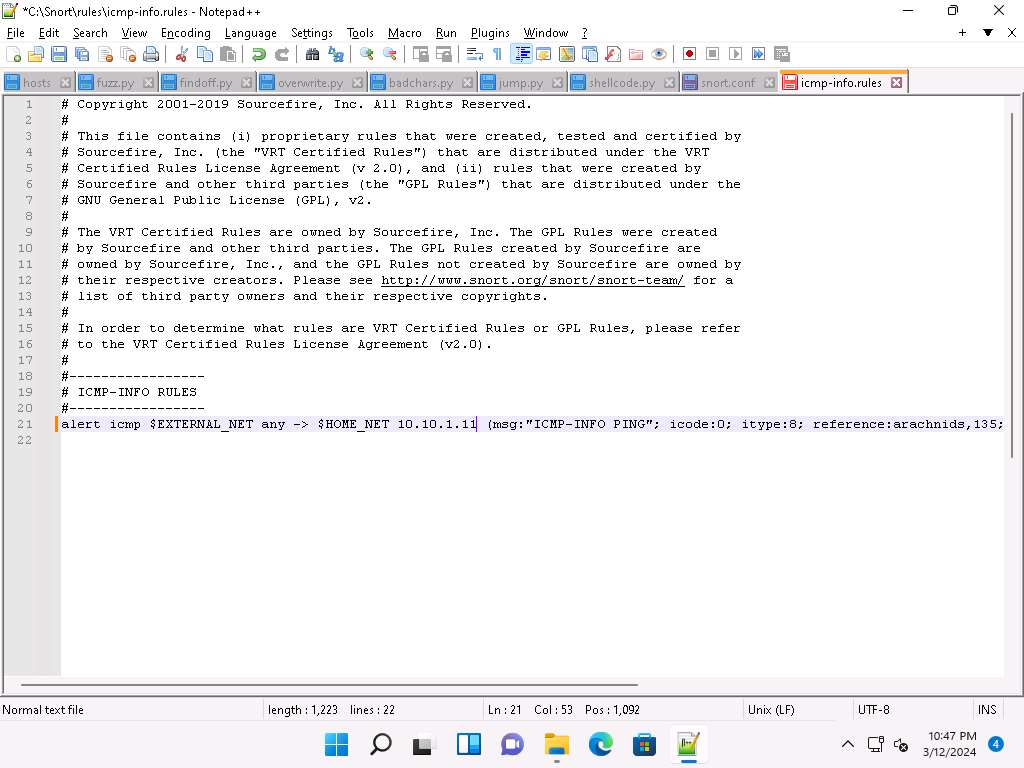
In line 21, type alert icmp HOME_NET 10.10.1.11 (msg:“ICMP-INFO PING”; icode:0; itype:8; reference:arachnids,135; reference:cve,1999-0265; classtype:bad-unknown; sid:472; rev:7;) and save. Close the Notepad++ window.
The IP address (10.10.1.11) mentioned in $HOME_NET may vary when you perform this task.
-
Now right-click on the Windows Start icon and click Run from the menu.
-
In the Run window, type cmd in the Open field and press Enter: This will launch a command prompt window.
-
In the command prompt window, type cd C:\Snort\bin and press Enter.
-
Run command snort -iX -A console -c C:\Snort\etc\snort.conf -l C:\Snort\log -K ascii to start Snort (replace X with your device index number; in this task: X is 1).

-
If you receive a fatal error, you should first verify that you have typed all modifications correctly into the snort.conf file, and then search through the file for entries matching your fatal error message.
-
If you receive an error stating “Could not create the registry key,” then run the command prompt as Administrator.
-
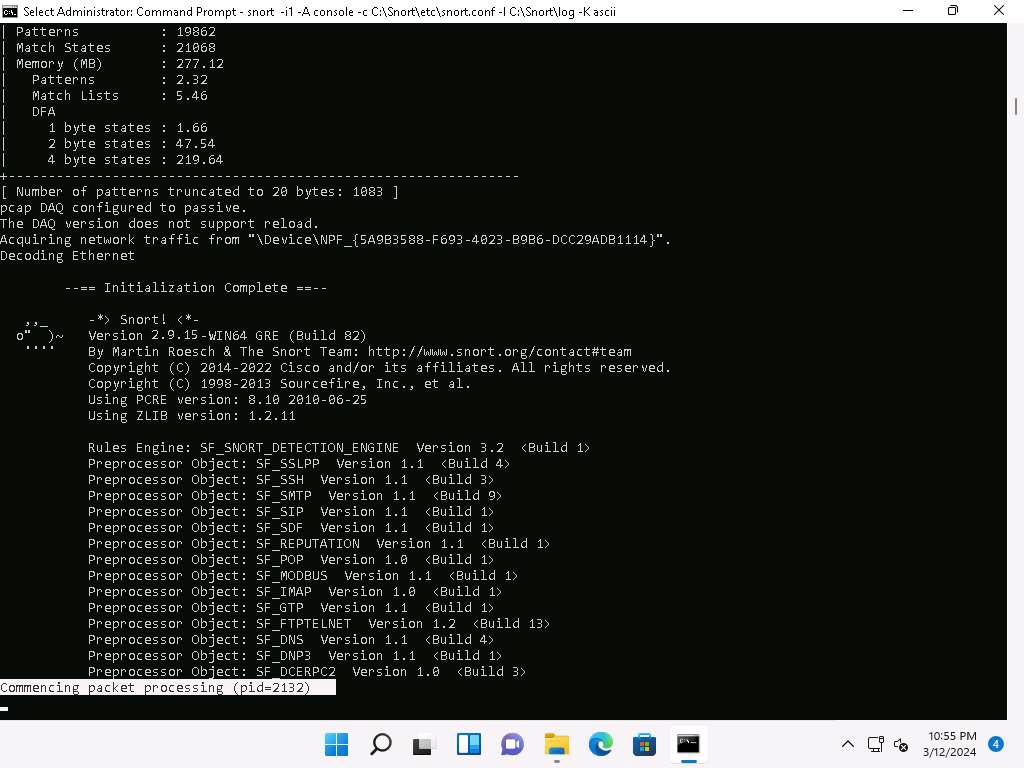
Snort starts running in IDS mode. It first initializes output plug-ins, preprocessors, plug-ins, loads dynamic preprocessors libraries, rule chains of Snort, and then logs all signatures.
-
If you have entered all command information correctly, you receive a comment stating Commencing packet processing (pid=xxxx) (the value of xxxx may be any number; in this task, it is 2132), as shown in the screenshot.
-
After initializing interface and logged signatures, Snort starts and waits for an attack and triggers alerts when attacks occur on the machine.
-
Leave the Snort command prompt running.
-
Attack your own machine, and check whether Snort detects it or not.
-
Now, click on Windows Server 2019 to switch to the Windows Server 2019 machine (Attacker Machine). Click Ctrl+Alt+Delete to activate the machine and login with Administrator/Pa$$w0rd.
-
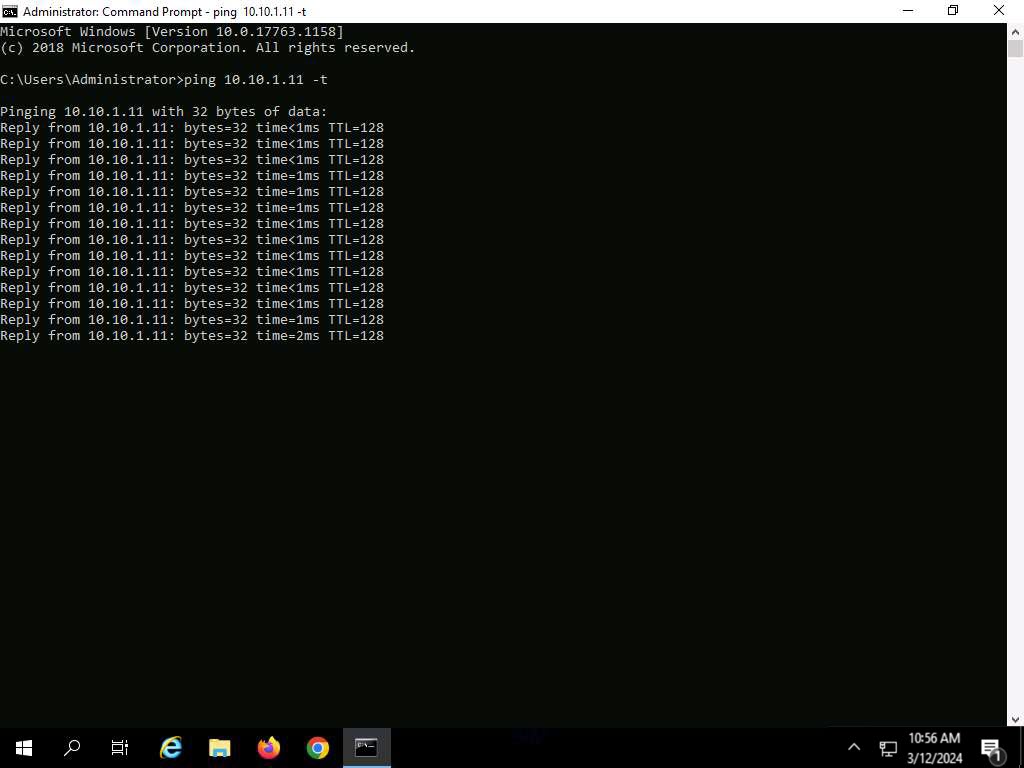
Open the command prompt and issue the command ping 10.10.1.11 -t from the Attacker Machine
10.10.1.11 is the IP address of the Windows11. This IP address may differ when you perform the task.
-
Click Windows 11 to return to the Windows 11 machine. Observe that Snort triggers an alarm, as shown in the screenshot:
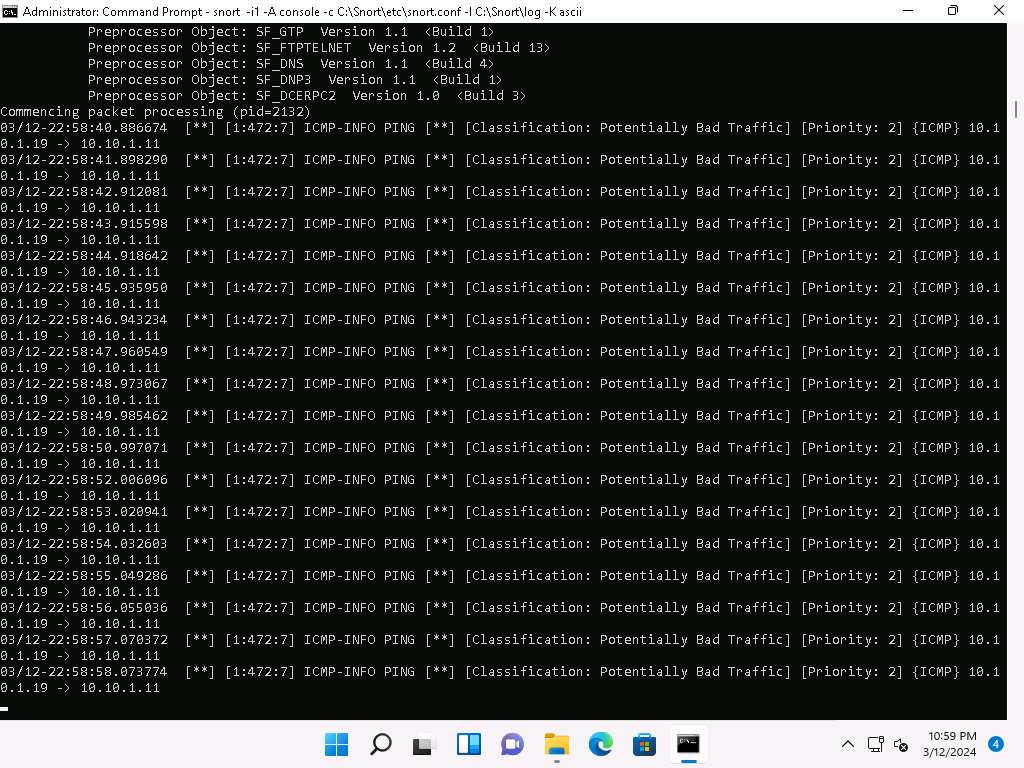
-
Press Ctrl+C to stop Snort; snort exits.
-
Go to the C:\Snort\log\10.10.1.19 folder and open the ICMP_ECHO.ids file with Notepad++. You see that all the log entries are saved in the ICMP_ECHO.ids file.
The folder name 10.10.1.19 might vary when you perform the task, depending on the IP address of the Windows 11 machine.
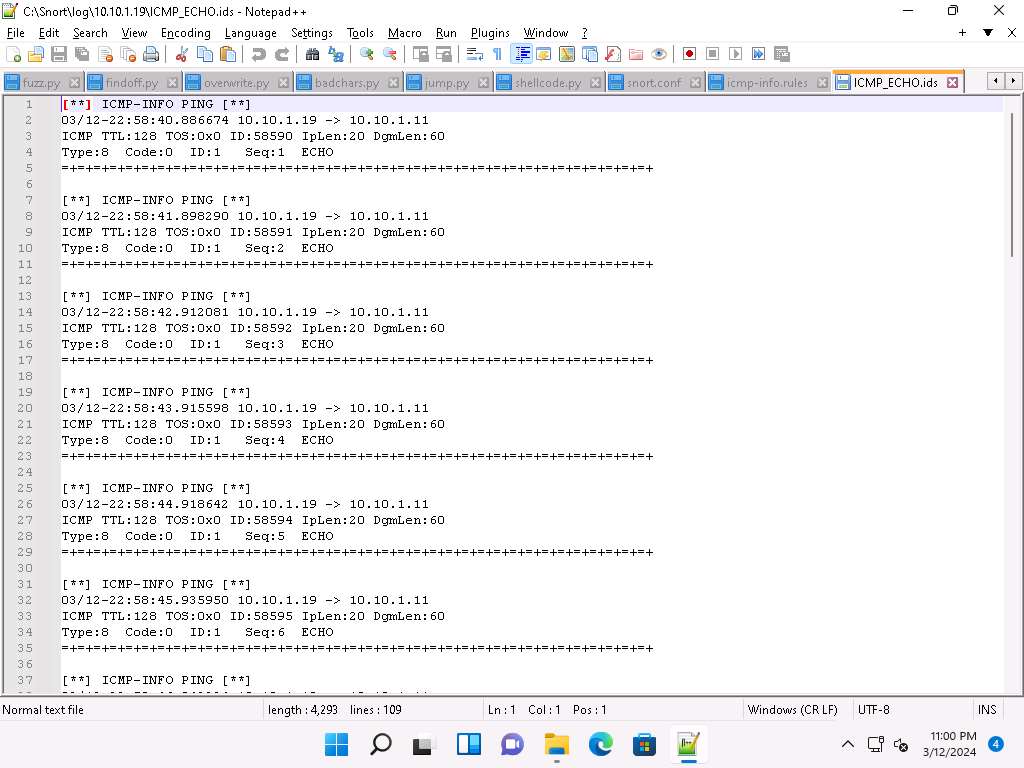
This means that whenever an attacker attempts to connect or communicate with the machine, Snort immediately triggers an alarm
This will make you aware of the intrusion and can thus take certain security measures to disconnect the lines of communication with the attacker’s machine.
-
Close all open windows in the Windows 11 and Windows Server 2019 machines.
Question 12.1.1.1
Install Snort in the Windows Server 2019 machine. The necessary files are available at Z:\CEHv13 Module 12 Evading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypots\Intrusion Detection Tools\Snort. Configure and initialize the Snort tool. Initialize the Snort interfaces and attack a target machine from the attacker machine (10.10.1.11) to check whether Snort detects it or not. Enter the Snort command to view the index number of the Ethernet driver.